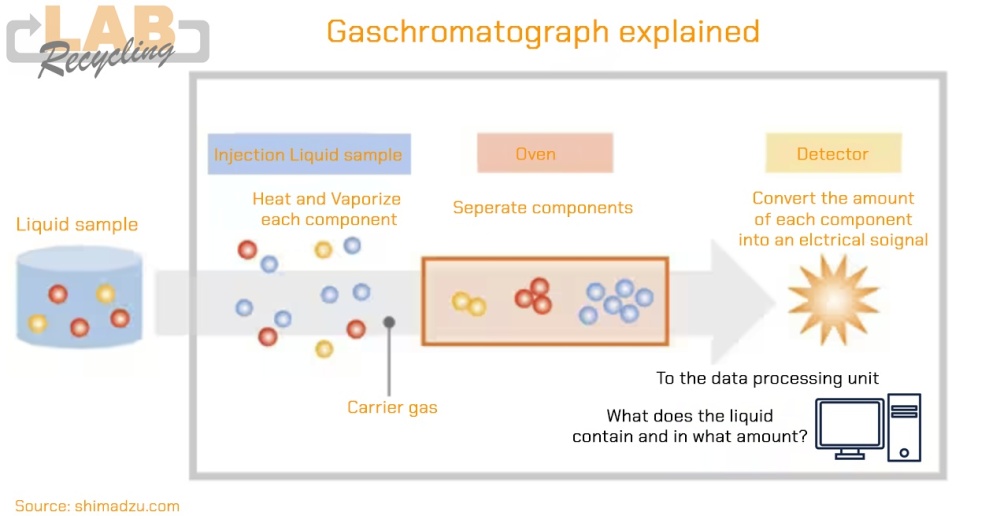
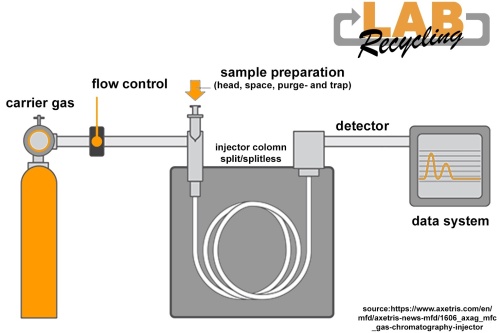
On this webpage we give you some more information how gas chromatography works.
How does Gas chromatography (GC) works?
Is an universal type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized, without decomposition.
It is based on a difference in the distribution of the substances to be separated between a liquid or solid stationary phase and a uniform gaseous mobile phase.
When do I use a GC?
Mostly for qualitative and quantitative analysis of food products, quantification of additives, identification of flavour and aroma compounds, and the detection of contaminants like pesticides and natural toxins.
Characteristic is the high analysis speed, the high resolving power and the accuracy.
Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture. These chemical components are usually organic molecules or gases.
GC was the most important separation technique, until....
Many years ago was Gas chromatography, analytical whise, the most important separation technique. But that changed in the last century. The importance of HPLC has increased in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Both methods complement each other to form a powerful and universal set of separation instruments.
There are various devices with, which you can perform the gas chromatography method. Many of these GCs are of the Brands: Agilent, Shimadzu, Perkin Elmer and Thermo.
4 types of detectors in a GC
1. Electron capture detector (ECD)for halogenated and aromatic compounds, as well as other analytes with high electron affinity.
2. Nitrogen-phosphorus detector (NPD)for compounds containing nitrogen or phosphorus.
3. Flame photometric detector (FPD)
for compounds containing sulfur or phosphorus.
4. Chemiluminescence detectorsfor compounds containing sulfur (SCD) or nitrogen (NCD).